

Vol. 40 (Number 35) Year 2019. Page 25
NATORINA, Alona 1
Received: 17/06/2019 • Approved: 09/10/2019 • Published 14/10/2019
ABSTRACT: In this study author justified that the decisive conditions for the sustainable online retailers’ development in the digital age are determined by innovation activity. According to this, the author systematized factors that hinder innovative activity realization and proposed the methodical approach to assessing the online retailers’ innovation activity. As a result of the methodological approach approbation, it is recommended for usage by online retailers to increase their competitiveness in the digital age. |
RESUMEN: En este estudio, el autor justificó que las condiciones decisivas para el desarrollo sostenible de los minoristas en línea en la era digital están determinadas por la actividad de innovación. De acuerdo con esto, el autor sistematizó los factores que obstaculizan la actividad innovadora y propuso el enfoque metódico para evaluar la actividad de innovación de los minoristas en línea. Como resultado de la aprobación del enfoque, se recomienda su uso para aumentar la competitividad en la era digital. |
Innovations are catalysts of the digital business development and competitiveness in the online market. Therefore, the solution of issues related to the management of innovation and innovation projects, as well as the relevant innovation activity implementation, is a priority for online retailers in the digital era.
In the digital era, it is very important for online retailers to adapt to the market, including actively implement innovations. Baird (2018) in his work “What digital transformation actually means for retail” described the main aspects of retailers’ activity in the digital transformation and emphasized the role of innovation for retailers.
Advantages and benefits for retailers in terms of digitalization are studied by Parviainen, Tihinen, Kaariainen, & Teppola (2017) in their work entitle “Tackling the digitalization challenge: how to benefit from digitalization in practice”. The authors also examine the question of the need for innovation in retail.
Bhave, Biggs, Burggraaff, Loftus, & Pathak (2018) from the Boston Consulting Group in their research “Accelerating digital innovation in retail” pointed a special attention to the need for the implementation of innovations in the retailers’ activities in the digital environment. In addition, a leading international public marketing company, Nielsen (2013) emphasized the importance of innovation activity for the successful retailers operation. Moreover, the specialists of this company argued that innovation activity must be permanent.
Thus, today there are a large number of publications about the importance and role of innovation for retailers. However, the question of assessing online retailers’ innovation activity still has not been fully studied in the digital age. It has defined the direction of this study.
The purposes of the article are to research and analyze the practical aspects of the implementation of online retailers’ innovation activity; to develop and test a methodological approach to assessing the online retailers’ innovation activity in the digital age.
The strategic vector of online retailers’ progressive development in the digital age is determined by the trend of their innovation activity. Online retailers, through the implementation of innovation in the digital age, can improve relevant areas of marketing activity, which is closely related to online customer satisfaction. This is the basis of effective relationships formation between online retailers and buyers.
Innovative activity represents the ability of online retailers and its frequency to decree rational decisions that serve as a criterion for success in the corresponding field. Innovation activity is extremely important for producing total innovation. It is possible due to effective interaction with online retailers’ departments, as well as stakeholders during generation and exchange of new ideas and creation / adjustment of the concept of the digital business development.
The level of innovation that relevant to the marketing environment accelerates the achievement of strategic goals and the implementation of operational tasks of online retailers.
According to international studies of Bernon, Cullen, & Gorst (2016); Doherty & Ellis‐Chadwick (2010) and Nordfalt, Grewal, Roggeveen, & Hill, (2014); a small number of online retailers are actively implement innovations. The explanation for this may be the high costs of innovation and, as a result, low innovation activity of the digital business.
The main factors hindering the implementation of innovative activity of enterprises in Ukraine is represented in Fig. 1.
Figure 1
The main factors hindering the innovative activity
implementation of Ukrainian enterprises
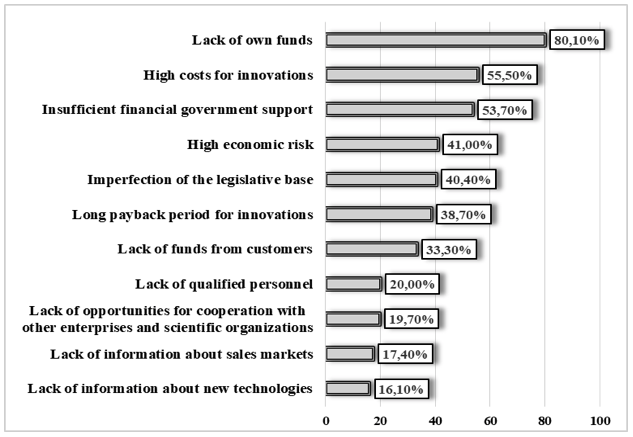
Source: Created by the author according to
the State Statistics Service of Ukraine (2019)
The percentages shown in Fig. 1 represent factors stated for the total number of companies surveyed. Therefore, the problem of the online retailers sustainable functioning in the digital age makes it necessary to stimulate their innovative activity.
Rational innovation management of online retailers in the digital age contributes to the improvement of their business processes and increases the level of needs satisfaction and preferences of online shoppers. This increases the market competitiveness level of online retailers and corrects the key performance indicators of their activities. Innovation activity allows online retailers to adapt to the new realities of doing business in the digital age, to introduce differentiated concepts of promotion, while maintaining the existing level of online shopper’s loyalty in an aggressive market competition.
In this study, a survey of Ukrainian experts in online retail was conducted and, as a result, the following postulates about online retailer’s innovation activity in the digital age are formulated:
As a result of research and analysis of international practice, it was identified the main mistakes in the assessment of online retailers’ innovation activity:
1. Excessive number of innovation activity metrics.
The complex system of metrics for the online retailers’ innovation activity is a significant expenditure of working time for collecting, processing and monitoring information. Such costs may be unacceptable for the interpretation and adoption of operational administrative decisions. In the digital era, metrics for assessment of online retailers’ innovation activity have to be correlated with the financial system and other exogenous metrics or, to perfection, be an integral part of such systems. Metrics for assessment of the innovation activity should be reasonable and practical. Only in this case managers will have the opportunity to establish reasonable values for the target metrics and develop constructive strategies for achieving it.
2. Project point of view about the innovation activity metrics.
In many cases, management of the online retailers’ innovation activity in the digital age is carried out on the project management basis. However, innovation activity is not a set of isolated projects. It is a continual process of initiation (generation) and selection of innovative ideas, which ends with the implementation of new projects. In this context, innovative ideas are springboard that forms the basis for inspiring new online services in addition to existing ones. Based on the above, the use of “project” metrics for assessment of online retailers’ innovation activity is impractical. For example, modern online retailers are actively working on the implementation of innovations for the convenience of buyers with disabilities. For example, the usage of online sign language interpreter in the Russia pharmacy retail. Also, the mobile applications integration is being used by retailers to optimize the online buying process. The new version of the “Leroy Merlin” (Ukraine retailer) mobile application allows online buyers to “try on” furniture and appliances from the store's range. To do this, it is necessary to use the application, select the product and choose "View in Augmented Reality".
3. Partial nature of the innovation activity metrics.
Due to the scale of coverage of online retailers in different marketing spheres, some departments develop and apply autonomous metrics for innovation activity assessment. Such metrics are not integrated into the corporate metrics system and are not considered by the management as strategically important. Therefore, these metrics for innovation activity assessment have partial nature.
4. Sporadic usage of the innovation activity metrics.
A high percentage of failure to achieve tactical goals may result in the refusal of management to implement a policy regarding the initiation (generation) of innovative ideas and the search for an optimal implementation solution. However, it is possible to reduce the risk of not achieving goals in the case of the correct implementation of domestic policy, which implies the positive attitude to innovations as to valuable experience. That is why, it is advisable to use the innovation activity metrics of online retailers in the digital age for comparative analysis with simultaneous development of incentive programs for personnel. Unforeseen negative results can be used as a valuable experience for the development of digital business in the long term. This management approach will indicate a desire to develop digital business through the ongoing innovation of online retailers.
Considering the above described, the author proposed to use the appropriate metrics for a comprehensive assessment of the online retailers’ innovation activity (J) in the digital age (1):
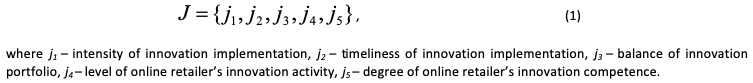
This metrics will help managers to reasonably allocate financial resources. Comparison of current metrics with metrics of previous periods will allow identifying business processes which financing does not correlate with the general strategic goal.
It is assumed that the assessment of the online retailers’ innovation activity metrics is carried out by online retail experts. Stages of the assessment of the online retailers’ innovation activity in the digital era:
1. Expert assessment of the proposed online retailers’ innovation activity metrics and assigning appropriate score – 0 or 1.
For the study, from the total number of Ukrainian retailers with the largest offline networks in four segments (food retail, drogerie, retail in the field of home appliances and electronics, do-it-yourself (DIY) retail); was selected those which implement online business. The entire set of 21 online retailers was divided into three clusters according to Natorina (2018) in the paper “Online retailers’ management system of marketing commodity policy”.
Cluster 1: Auchan Ukraine (FR1), Metro Cash and Carry Ukraine (FR2), NOVUS Ukraine (FR4), DC Ukraine (DR1), RUSH (DR2), ALLO (HA1), Foxtrot (HA2), DIESA (HA3), Comfy Trade (HA4), NRP (HA5), Citrus Discount (HA6), Leroy Merlin Ukraine (DIY5).
Cluster 2: NASH KRAI (FR3), Tavria V (FR5), Fozzy Food (FR6), Budmax (DIY3).
Cluster 3: BRV Kyiv (DIY1), Nova Linia (DIY2), Epicentr K (DIY4), Furniture Company of Ukraine (DIY6), JYSK Ukraine (DIY7).
The division into clusters was carried out as a result of the assessment of online retailers marketing policies by online buyers. Among the metrics of the assessment were type of interaction with online buyers; frequency of online shopping; the level of competitiveness of the commodity portfolio and the quality of goods, between others.
Proposed online retailers’ innovation activity metrics is presented below with the appropriate standardized scale that was developed by using the expert assessments (Table 1).
Table 1
The scale of the expert
assessments standardization
No |
Metrics |
Score |
|
0 |
1 |
||
1 |
Intensity of innovation implementation |
low |
high |
2 |
Timeliness of innovation implementation |
yes |
no |
3 |
Balance of innovation portfolio |
yes |
no |
4 |
Level of online retailer’s innovation activity |
low |
high |
5 |
Degree of online retailer’s innovation competence |
low |
high |
Source: Developed by the author
2. Construction of the binary matrix based on the results of experts’ assessment of online retailers’ innovation activity.
3. Identification of the consistency of experts’ opinions by determining the coefficient of concordance (Kcom). In our case, considering the fact that Kcom>0.5 (Kcom=0.8), so the opinions of the experts are consistent.
4. Calculation of the total experts scores for each 5 metrics, which demonstrates its significance. The determination of weight coefficients (xj) for each 5 metrics as the ratio of the total metric score to the total score (J).
The calculation of the weight coefficients of the online retailers’ innovation activity metrics is shown in the Table 2.
Table 2
The weight coefficients of the
online retailers’ innovation activity
No |
Metrics |
Designation |
Expert score |
Total metric score |
Weight coefficient (xj) |
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|||||
1 |
Intensity of innovation implementation |
j1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0.118 |
2 |
Timeliness of innovation implementation |
j2 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
0.176 |
3 |
Balance of innovation portfolio |
j3 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
0.176 |
4 |
Level of online retailer’s innovation activity |
j4 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
0.294 |
5 |
Degree of online retailer’s innovation competence |
j5 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
4 |
0.235 |
Totalscore |
J |
4 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
17 |
1.000 |
|
Source: Calculated by the author
According to Table 2, the Level of online retailer’s innovation activity has the biggest impact on online retailers' innovation activity. This describes the willingness to make effective management decisions regarding the introduction of relevant innovations to ensure the steady and stable functioning of online retailers. Degree of online retailer’s innovation competence has a slightly smaller impact. This is because the result of the online retailers’ innovative activity depends on the knowledge and skills of the staff. Timeliness of innovation implementation and Balance of innovation portfolio have an equal impact. This is due to the effectiveness of the implementation of measures in response to the actions of online retailers’ competitors. The Intensity of innovation implementation has the least impact on the online retailers’ innovation activity. This is due to the specifics of online retailers and market conditions.
5. Calculation of the weighted average score of the online retailers’ innovation activity (2):
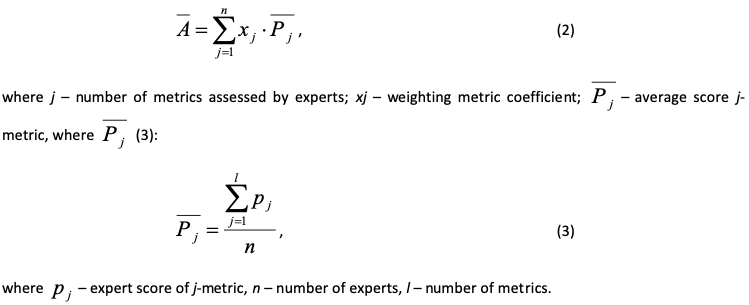
The Table 3 presented the results of the experts' assessment (April, 2019) and the weighted average scores of online retailers' innovative activity metrics in clusters.
Table 3
The assessment of the online retailers’
innovation activity metrics in clusters
Cluster |
Online retailer |
Average expert score |
Weighted average score ( ) |
||||
j1 |
j2 |
j3 |
j4 |
j5 |
|||
Cluster 1 |
FR1 |
4.800 |
4.600 |
5.000 |
5.000 |
4.800 |
4.859 |
FR2 |
4.400 |
4.000 |
4.400 |
4.400 |
4.800 |
4.424 |
|
FR4 |
4.200 |
4.000 |
4.600 |
4.000 |
4.800 |
4.318 |
|
DR1 |
4.000 |
3.400 |
3.800 |
3.800 |
4.400 |
3.894 |
|
DR2 |
4.000 |
3.600 |
3.800 |
4.400 |
4.000 |
4.012 |
|
HA1 |
5.000 |
4.600 |
5.000 |
4.800 |
5.000 |
4.871 |
|
HA2 |
5.000 |
4.600 |
4.600 |
4.800 |
5.000 |
4.800 |
|
HA3 |
4.200 |
4.400 |
4.000 |
4.000 |
4.800 |
4.282 |
|
HA4 |
4.800 |
5.000 |
5.000 |
5.000 |
5.000 |
4.976 |
|
HA5 |
4.200 |
4.200 |
4.000 |
3.800 |
4.000 |
4.000 |
|
HA6 |
5.000 |
5.000 |
5.000 |
4.800 |
4.800 |
4.894 |
|
DIY5 |
5.000 |
4.800 |
4.800 |
4.600 |
5.000 |
4.812 |
|
Average score |
4.550 |
4.350 |
4.500 |
4.450 |
4.700 |
4.512 |
|
Cluster 2 |
FR3 |
2.200 |
2.400 |
2.400 |
2.200 |
2.800 |
2.412 |
FR5 |
2.600 |
2.800 |
2.000 |
2.600 |
3.000 |
2.624 |
|
FR6 |
3.000 |
3.000 |
2.800 |
2.600 |
3.600 |
2.988 |
|
DIY3 |
3.800 |
3.400 |
3.400 |
3.400 |
4.200 |
3.635 |
|
Average score |
2.900 |
2.900 |
2.650 |
2.700 |
3.400 |
2.915 |
|
Cluster 3 |
DIY1 |
3.600 |
3.800 |
3.000 |
3.000 |
3.800 |
3.400 |
DIY2 |
4.000 |
4.000 |
4.200 |
3.400 |
4.600 |
4.000 |
|
DIY4 |
4.400 |
4.600 |
4.400 |
4.000 |
5.000 |
4.459 |
|
DIY6 |
3.800 |
3.000 |
3.000 |
3.000 |
4.000 |
3.329 |
|
DIY7 |
4.200 |
4.000 |
3.400 |
3.600 |
4.400 |
3.894 |
|
Average score |
4.000 |
3.880 |
3.600 |
3.400 |
4.360 |
3.816 |
|
Source: Calculated by the author
The graphic interpretation of the generalized results of the calculations of the average metrics scores in the context of online retailers’ clusters is shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2
Average scores of the online retailers’
innovation activity metrics in clusters

Source: Created by the author
According to Figure 2 there is a slight gap in all of the average expert scores of Cluster 1 and Cluster 3, as well as the significant gap between Cluster 1 and Cluster 2. This testifies the active realization of the online retailers’ innovation activity of Cluster 1, which predetermines rapid progressive development in the context of changes in the socio-cultural environment of online buyers and allows them to consolidate market positions due to the steady demand for goods and services. Online retailers’ of Cluster 3 show the feasibility of focusing managers on the development of appropriate marketing plans and activities. This will allow to online retailers to take advantages of the rational organization of innovation activity in the market. The low average expert scores of the metrics of Cluster 2 shows the lack of interest among online retailers to implement innovation activity, including innovative technologies to expand the target audience and ensure its varied requests, needs, and preferences. In view of the above, it is appropriate for these online retailers to focus on the introduction of innovation activities that will catalyze qualitative changes and lead to improved commercial results. Considering the above, it is advisable for these online retailers to focus on the active realization of innovation, catalyze qualitative changes and lead to improved business results.
According to the results of calculations (Table 3), of online retailers that formed Cluster 2 are the lowest in comparison with Cluster 1 and Cluster 3. In turn, of online retailers, that formed Cluster 1, are the highest. This in general represents the results of the calculations of the average expert score of the metrics of the online retailers’ innovation activity in clusters (Table 3, Figure 2).
Intensity and timeliness of innovation implementation affect the satisfaction of the actual needs of customers, which is directly related to the marketing activities of online retailers. Balance of innovation portfolio helps to increase the quantity of potential online buyers and the expansion of new markets. Moreover, marketing activities also contribute to similar goals. The level of innovation activity affects the online retailers’ competitiveness. And systematic and integrated implementation of marketing activity, in this case, helps to strengthen the position of online retailers. Therefore, it should be noted that the online retailers’ innovation activity are related to their marketing activities.
Yohn (2019), who is a leading marketing expert in her article (“Why great innovation needs great marketing”) noted that innovation is a top priority for almost every organization. But to achieve success through innovation, companies must put as much energy and investment into marketing new offerings as they do in generating them. The role of marketing in some companies seems to have diminished in recent years, with the growth of artificial intelligence-driven algorithms and predictive analytics. Understanding people’s fundamental needs and drivers, identifying customers, and developing the entire go-to-market and usage ecosystem are the essential aspects of marketing – and the ones that the success of innovations, especially breakthrough ones, hinge upon. Marketers need to be included in development discussions earlier in the innovation process. Innovation alone may be enough to initiate the adoption life cycle, but marketing remains the bridge necessary to cross the chasm between early adopters to the wider group of people who will form a viable, valuable customer base. The bigger the innovation, the bigger the risk of failure. Because marketing can reduce those risks, it matters as much as innovation – perhaps even more.
Importantly, that the famous professor and management consultant Drucker (2014) in his work “Innovation and entrepreneurship”, defined innovation as the task of endowing human and material resources with new and greater wealth producing capacity. He was sure that it is not confined to separate business functions but extends across all activities of the enterprise; it provides the means to convert society's needs to profitable business opportunities. Only marketing and innovation produce revenue. All other business functions produce costs.
Based on the above, it can be formulated the following conclusions: The primary basis for the implementation of online retailers’ innovation activity is the relevant perception of new market opportunities in order to design a new service or business process to meet the demands, needs, preferences of online consumers. Correct marketing focus is the determinant of the successful commercialization of innovation. Therefore, the use of marketing tools and technologies, including the selection of promising market segments for the implementation of dynamic online sales, plays an important role for online retailers’ innovation activity.
It is important to highlight that the assessment of online retailers’ innovation activity does not provide an opportunity to make an in-depth analysis of the current level of marketing tools and technologies usage for:
(1) getting the most positive result when making administrative decisions to improve the efficiency of online functioning,
(2) determination of the future trajectories of online retailers – persistent, integrative and coadaptive trajectories.
Detailed descriptions of trajectories, which proposed by Natorina (2018), interpreted in the article “The marketing commodity policy of online-retailers: characterization and trajectories of development”.
Considering above, the qualifying classifier to assessing online retailers’ innovation activity in the digital is proposed (Table 4), taking into account the features of marketing tools and technologies usage.
Table 4
The qualifying classifier to assessing online
retailers’ innovation activity in the digital age
Range of A |
Qualitative linguistic rating |
Explication of qualitative linguistic rating |
0 ≤ A < 1.667 |
Passive (P) |
The lack of practice in the systematic use of marketing tools and technologies in the implementation of innovation. This is due to the inability of the online retailer to implement an adaptation policy in modern changes in market conditions, including a shortage of highly qualified specialists in marketing. In such conditions, it is advisable for an online retailer to analyze staff competence and conduct comprehensive diagnostics of human resources for social development. Moreover, it is recommended to develop a plan for the realization of innovative activity using marketing tools and technologies. |
1.667 ≤ A < 3.333 |
Focused (F) |
Fragmentary use of marketing tools and technologies by online retailers in the implementation of innovative activity. This is due to the focus on a certain market segment / irradiation of the regular online buyers or the desire of augmentation of sales in the corresponding period. Such an assessment for a long time may indicate the futility of the marketing tools and technologies chosen by the management and lead to disharmonious development of all constituents of online marketing activity. |
3.333 ≤ A ≤ 5.000 |
Active (А) |
Active permanent usage of marketing tools and technologies by online retailers is an integral part of the successful implementation of innovation. The effectiveness of this symbiosis is explained by the improvement of competitive market positions in tough aggressive competition. It contributes to the rapid transformation of online retailers according to the interference of marketing factors. |
Source: Developed by the author
According to the calculations (Table 3) and proposed qualifying classifier to assessing online retailers’ innovation activity (Table 4), the qualitative linguistic rating for each online retailer is determined (Table 5).
Table 5
The qualitative linguistic ratings of online retailers’ innovation activity in clusters
Cluster |
Online retailer |
A |
Qualitative linguistic rating |
Cluster |
Online retailer |
A |
Qualitative linguistic rating |
Cluster 1 |
FR1 |
4.859 |
A |
Cluster 2 |
FR3 |
2.412 |
F |
FR2 |
4.424 |
А |
|||||
FR4 |
4.318 |
А |
FR5 |
2.624 |
F |
||
DR1 |
3.894 |
А |
|||||
DR2 |
4.012 |
А |
FR6 |
2.988 |
F |
||
HA1 |
4.871 |
А |
|||||
HA2 |
4.800 |
А |
DIY3 |
3.635 |
А |
||
HA3 |
4.282 |
А |
Cluster 3 |
DIY1 |
3.400 |
А |
|
HA4 |
4.976 |
А |
DIY2 |
4.000 |
А |
||
HA5 |
4.000 |
А |
DIY4 |
4.459 |
А |
||
HA6 |
4.894 |
А |
DIY6 |
3.329 |
F |
||
DIY5 |
4.812 |
А |
DIY7 |
3.894 |
А |
Source: Calculated by the author
According to the Table 5 it can be seen that the online retailers of Cluster 1, Cluster 3 (except DIY6) and DIY3, which is part of Cluster 2, are actively using marketing tools and technologies. Online retailers of Cluster 2 (except DIY3) carry out focused innovation activity, involving the fragmentary usage of marketing tools and technologies. The calculations indicate a high level of online retailers’ innovation activity in the digital era. They are leaders in the relevant market segment. In addition, it should be mentioned that DIY3 implements new technologies for productive online activity and increases its potential for sustainable progressive development in the future.
It was found that the decisive condition for the sustainable development of online retailers in the digital age is determined by innovation activities. The correlation between the marketing and innovation activities of online retailers is interpreted. Based on the international practice studies, the author proposed the methodical approach to assessing the online retailers’ innovation activity in the digital age. Approbation of the methodological approach is carried out by the example of Ukrainian online retailers. As a result of the methodological approach approbation, the determinatively qualitative linguistic assessments of online retailers’ innovation activity are determined. The methodical approach is recommended for usage by online retailers. Implementation of the approach will increase the online retailers’ competitiveness in the digital age. It will also contribute to the formalized base formation of alternative management decisions for online retailers.
Baird, N. (2018). What digital transformation actually means for retail. Forbes. Retrieved May 12, 2019, from from https://www.forbes.com/sites/nikkibaird/2018/03/13/what-digital-transformation-actually-means-for-retail/#7e24e8eb7038
Bernon, M., Cullen, J., & Gorst, J. (2016). Online retail returns management: Integration within an omni-channel distribution context. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 46(6/7), pp. 584-605. doi:https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPDLM-01-2015-0010
Bhave, A., Biggs, C., Burggraaff, P., Loftus, B., & Pathak, S. (2018). Accelerating digital innovation in retail. The Boston Consulting Group. Retrieved May 12, 2019, from http://image-src.bcg.com/Images/BCG-Accelerating-Digital-Innovation-in-Retail-June-2018_tcm9-194430.pdf
Catalogue of Official Statistical Publications. (2019). Retrieved March 25, 2019, from State Statistics Service of Ukraine: http://ukrstat.org/en
Doherty, N., & Ellis‐Chadwick, F. (2010). Internet retailing: the past, the present and the future. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 38(11/12), pp. 943-965. doi:https://doi.org/10.1108/09590551011086000
Drucker, P. (2014). Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practice and Principles. New York: Routledge.
Natorina, A. (2018). Online retailers’ management system of marketing commodity policy. Economic Annals-XXI, 174(11-12), pp. 69-72. doi:https://doi.org/10.21003/ea.V174-11
Natorina, A. (2018). The marketing commodity policy of online-retailers: characterization and trajectories of development. Business Inform, 9, pp. 272-277. Retrieved from http://www.business-inform.net/export_pdf/business-inform-2018-9_0-pages-272_277.pdf
Nielsen. (2013). Continuous innovation: the key to retail success. Retrieved April 3, 2019, from https://www.nielsen.com/content/dam/nielsenglobal/eu/nielseninsights/pdfs/Continuous%20Innovation%20The%20Key%20to%20Retail%20Success.pdf
Nordfalt, J., Grewal, D., Roggeveen, A., & Hill, K. (2014). Insights from In-store Marketing Experiments. Review of Marketing Research: Shopper Marketing and the Role of In-Store Marketing, 11, 127-146.
Parviainen, P., Tihinen, M., Kaariainen, J., & Teppola, S. (2017). Tackling the digitalization challenge: how to benefit from digitalization in practice. International Journal of Information Systems and Project Management, 5(1), pp. 63-77. doi:https://doi.org/10.12821/ijispm050104
Yohn, D. L. (2019). Why great innovation needs great marketing. Retrieved April 19, 2019, from https://hbr.org/2019/02/why-great-innovation-needs-great-marketing
1. PhD (Economics), Acting Head of the International Economics, Accounting and Finance Department, Academician Yuriy Bugay International Scientific and Technical University, Kyiv, Ukraine. Contact e-mail: alyonanatorina@gmail.com