

Vol. 39 (Number 14) Year 2018 • Page 15
Ruslan A. ABRAMOV 1; Andrey P. KOSHKIN 2; Maksim S. SOKOLOV 3; Meir N. SURILOV 4
Received: 10/01/2018 • Approved: 31/01/2018
ABSTRACT: Actuality of the article is the integrative processes that require significant development and progressive unity to obtain a synergistic effect. Innovation thus defined as the leading framework for defining collaboration between States. It is shown that the feature of development and formation of the national innovation system in the framework of the Union State is based on the principles of administration in public space. The authors show that innovation in public administration form the special form for the design of future construction of a single economic space. It is noted that integration within the Eurasian Union is largely disproportionate and leads only to the division of innovation on infrastructure and private nature. The subject of the research is the innovation system of Russia and Belarus and the potential of a single innovation system in the framework of the Union state. Novelty of the work is the provision that public administration is a support function for the formation of innovation system in the state. The authors note that each of the participants for innovative cooperation may use only a few forms of participation. It is noted that full development of the capacity to form a holistic integrated innovation system is possible if the process provided by the public administration. The prospect of further studies is to predict the quality of cooperation between States: increasing the share of innovative products in the total turnover of the Union State and planning of joint production of innovative products. |
RESUMEN: El artículo estudia los procesos integradores que requieren un desarrollo significativo y una unidad progresiva para obtener un efecto sinérgico. La innovación así definida como el marco líder para definir la colaboración entre los Estados. Se muestra que la característica del desarrollo y la formación del sistema nacional de innovación en el marco del Estado de la Unión se basa en los principios de la administración en el espacio público. Los autores muestran que la innovación en la administración pública es la forma especial para el diseño de la futura construcción de un espacio económico único. Se observa que la integración dentro de la Unión Euroasiática es en gran medida desproporcionada y solo conduce a la división de la innovación en la infraestructura y la naturaleza privada. El tema de la investigación es el sistema de innovación de Rusia y Bielorrusia y el potencial de un sistema único de innovación en el marco del estado de la Unión. La novedad del trabajo es la disposición de que la administración pública es una función de apoyo para la formación del sistema de innovación en el estado. Los autores señalan que cada uno de los participantes en la cooperación innovadora puede usar solo algunas formas de participación. Se observa que el desarrollo completo de la capacidad para formar un sistema integral de innovación integral es posible si el proceso lo proporciona la administración pública. La perspectiva de nuevos estudios es predecir la calidad de la cooperación entre los Estados: aumentar la proporción de productos innovadores en el volumen de negocios total del Estado de la Unión y planificar la producción conjunta de productos innovadores. |
The concept of "innovative development", "innovation" in some way associated with the concept of "risk", which affects the methodology for the development of any management decision that relates to innovative development of national innovation systems.
The increase in the number of bankruptcies of various types of crisis situations in the sphere of innovations have become commonplace features of today. The entities of the Federal States of such phenomena and situations begin to talk and think to overcome them only when they are already a reality, and gradually acquire catastrophic proportions. Therefore, the first place took problem of prediction of crisis developments, events, situations, search of directions of its solving, the formation of the preventive measures of their prevention and overcoming, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of strategic management of innovative development of national innovation systems in General. In such cases, time is flexible, sensitive to changes in the external environment, the organizational structure of public administration. In the management of innovative development of national innovation systems mainly focuses on solving issues related to unpredictability, lack of clear delegation of authority, distribution of functions between the participants of innovation process national innovation systems in the long term.
An important feature of management of innovative development of national innovation systems is to ensure the elimination of obstacles for innovation development in order to avoid threats and crisis situations in activity of subjects of national innovation systems.
Management removing obstacles to innovative development is a set of forms and methods of realization of administrative procedures not only in relation to specific innovation project, but also the innovative activity of subjects of national innovation systems as a whole to ensure the elimination of threats and obstacles for innovation development.
Management strategy removing barriers to innovative development of national innovation systems – a set of actions and a sequence of managerial decisions that give the opportunity to analyse and assess the threats and obstacles to the innovative development and select the required system impact on improving the company to prevent its bankruptcy (Chlivickas and Melnikas, 2016, p. 118-123).
The policy of removing obstacles to innovative development, General direction of management actions of subjects of national innovation systems, a set of principles, methods, forms of organizational behavior, innovative update of the feasibility condition of subjects of national innovation systems, formation of a control system that can respond to constantly changing market conditions using innovative strategies (Sokolov, 2016, p. 11-16).
It can be argued that management remove obstacles to innovative development is a well – organized management, which is focused on prompt disclosure of the characteristics of the obstacles to innovative development and to create prerequisites for continuous tracking and timely overcome to ensure recovery of resilience actors in the national innovation systems in the innovation field, avoid situations leading to bankruptcy (Butyagin and Simkin, 2011, p. 267-268).
In our opinion, management elimination of obstacles for innovation development can be identified with the appropriate management and to determine how the control system of subjects of national innovation systems, which has a complex systemic nature (Nuti, 2007, p. 87-99). It is aimed at preventing or addressing adverse for innovative development of phenomena, events and situations through the use of the full potential of modern management, development and implementation of specific programmes with a strategic nature, which makes it possible to avoid possible temporary predicament, to preserve and enhance market positions by developing innovative products and innovative development of the economic entity of national innovation systems in General (Yekelchyk, 2008, p. 123) (see Fig. 1).
Figure 1
The control subsystem removing obstacles to innovative development
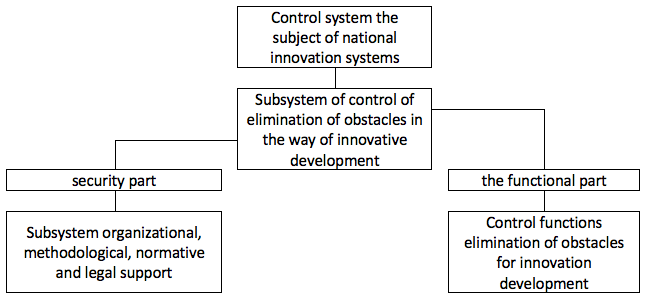
Source: developed by the author
The process of managing the elimination of barriers to innovative development involves the allocation of its elements (Kelley, 2016, p. 43):
The allocation of such items, in our opinion, reflects the essence of management by removing obstacles to innovative development, because it successfully focuses on the analysis of the macro and micro environments, the selection of the best of the mission entities, as the initial stage of management of innovation development (Pyun and Edey Gamassou, 2017, p. 67). In this phase, entities of public administration must recognize the potential obstacles that can appear in the process of functioning and development of subjects of national innovation systems (Vymyatnina and Antonova, 2014, p. 59).
At the moment in the Union State signed a partnership agreement between the Brest regional Executive Committee and administration of the Penza region, the agreement on trade-economic, scientific-technical and cultural cooperation between the Vitebsk oblast Executive Committee and the administration of the Saratov region, the agreement on cooperation between Vitebsk oblast and Stavropol Krai. Signed an action plan to intensify cooperation between Belarus and Bryansk region for 2017-2018 and the plan of measures on development of cooperation in 2017-2019 between Brest oblast and the Bryansk region. Both countries have programs of innovative development, but they do not overlap to a significant extent. You need to determine the basis for the formation of counter such differentiation on the level of the Union State.
The control subsystem removing obstacles to innovative development is part of a control system of the subjects of the national innovation systems and should include providing and functional parts (Abramov and Sokolov, 2017, p. 18-32). The first part consists of a subsystem of the organizational, methodological, regulatory and legal support. The functional part is combined the functions of management constraints (Czerewacz-Filipowicz and Konopelko, 2017, p. 63-64). This part is a set of economic and organizational methods and activities that ensure the solution of problems of diagnostics of a financial condition of subjects of national innovation systems, monitoring, warning and prevent the appearance of obstacles, the overcoming of the state of insolvency.
The main task of the control plane constraints to the innovative development is the development and acceptance of administrative decisions with minimal risk and additional resources, with minimal negative effects attain the objectives pursued and the expected results. Implementation this task involves the following subtasks management elimination of obstacles for innovation development:
‒ diagnosis and estimation of parameters of occurrence of interference;
‒ development of the concept and the corresponding set of measures to overcome the barriers through the implementation of appropriate strategic and operational actions;
the implementation of this concept in the process of removing obstacles;
‒ permanent monitoring of external and internal factors of the process of eliminating clutter.
Figure 2
Structural content management subsystem by
removing obstacles to innovative development
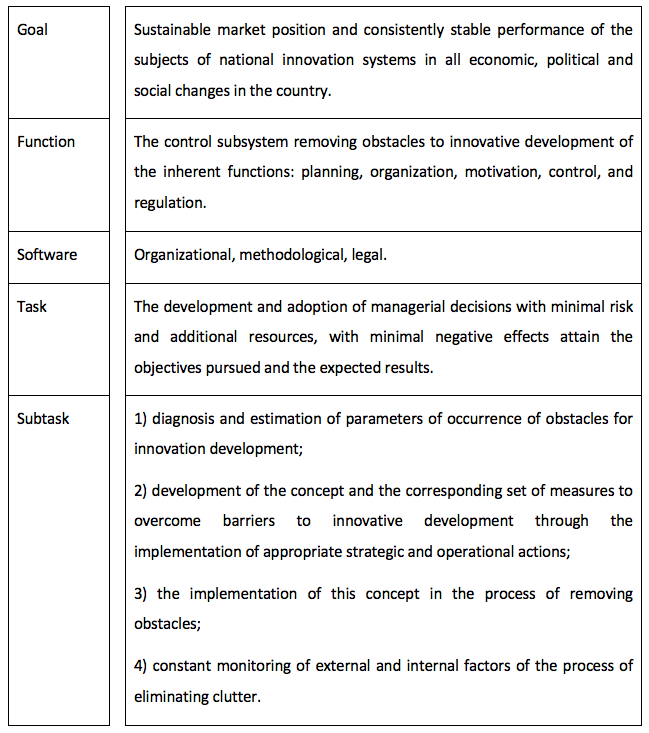
Source: developed by the author.
The main purpose of the control constraints is to ensure conditions for receiving and maintaining a sustainable market position, stable financial results of activity of subjects of national innovation systems in all socio-economic and political changes in the country.
The control subsystem removing obstacles to innovative development must be created along with the beginning of the creation of the subject of the national innovation system. At the very beginning of the system should be provided for creating various types of obstacles.
We believe that the control subsystem removing obstacles to innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems has the same function as conventional management: planning, organization, motivation, control and regulation.
Planning primarily involves the development of strategies and tactics to achieve established goals and objectives, plans and schedules the implementation of some measures aimed at achieving a particular goal the removal of obstacles to the innovative development and elaboration of complex of measures on financial improvement of the process of innovation. In the case of control constraints dramatically increases the role of operational planning and decision-making given the current situation.
The implementation of the planning function is based on the development of various plans which can be categorized by the following characteristics (White and Feklyunina, 2014, p. 93):
‒ the object of planning (the action plan for removing obstacles to innovative development, implementation plan, elimination of obstacles);
‒ term planning (operational, short, medium);
‒ planning scale (in General, for business entities, its departments, activities);
‒ planning (financial recovery plan, marketing plan, plan of diversification of productive activities and the like).
Organization – the phase in which provide the practical realization of the adopted plans for financial support of the innovation process and the elimination of obstacles for innovation development, that is responsible for the process of their implementation (Rudling, 2008, p. 28). The function of the organisation during carrying out of measures to remove obstacles to innovative development necessitates the creation of a staff of actors in the national innovation systems of professionals who strive to keep the organization and process of innovation (Bakanova and Freinkman, 2006, p. ). Thus, there is a necessity of documentary confirmation of an approved order (plan of action) making available to the staff and clear tasks to each employee and establish an integrated process control (Savchishina, 2014, p. 409-422).
Despite the properties, special moments in the implementation of innovative actions and measures for elimination of obstacles that require a lot of voltage and competence, an important condition arises forecasting system of incentives for groups that are engaged in the detection of obstacles, crises, pre-warning and response.
At the stage of control is provided by verification of compliance of the innovation process the established indicators of the financial recovery plan and involves the development of standards for the course in the form of a certain system of quantitative indicators to check the effectiveness and efficiency of individual measures of noise elimination, to make timely changes to them (Titu, 2016, p. 921-936).
In addition to the above control features, removing obstacles to innovative development places special emphasis on the diagnosis of irregularities and threats of innovative development of the subject of national innovation systems. Diagnostics gives the possibility to assess the probability of the current (operational) financial accounting and reporting (Bauer et al., 2017, p. 13-25). It appears the basis for hypotheses, new ideas concerning phenomena, of regularities in the possible changing economic and financial condition of a business entity. A particular utility it can bring into the elimination of obstacles for innovation development, which may be of varying depth, to take a wide range of financial and economic problems encountered by actors of national innovation systems and to be explicit and hidden (implicit).
Diagnostics consists of the following steps: monitoring, rapid diagnosis and fundamental diagnosis. The monitoring is carried out for early detection of characteristics of characteristics of obstacles, threats to innovative development, continuous accumulation of data and information through "weak signals" that are necessary for the implementation of the Express diagnostics. From the frequency of the holding of such a diagnosis depends on the quality of the information required for timely and effective management decisions and removing obstacles. The purpose of Express-diagnostics is a clear assessment of financial support, the dynamics of development and innovation, emergence and the removal of obstacles. It complements and konkretisiert fundamental diagnosis, which clarifies the level of noise identify the causes of their appearance (Ugyel, 2016, p. 44).
For owners and management the diagnosis is a means of obtaining reliable qualitative information about its real possibilities in the initial stage of occurrence of interference and the basis for the introduction of special methods and mechanisms of management (Stroev et al., 1999, p. 18-28). Considering all the results of the diagnostics generated preventive measures different aspects of innovative activity of subjects of national innovation systems, the owners and top managers initiate the formation of so-called reflexive control models removing barriers to innovation development.
So, thanks to diagnostics, you receive the possibility of identifying causal relations in management functions (Quinot, 2016, p. 93). In addition, it contributes to the formation of explanatory and predictive models of innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems, realizing at the same time preventing the occurrence of interference and bankruptcy (Smorgunov, 2016, p. 99).
In the process of developing a project management subsystem, removing obstacles to innovative development it is important to determine the functions. According to the methodology, these functions are typical of a General nature (forecasting, planning, coordination, motivation, analysis, accounting, control, organization, management) and dependence on specific types of subsystems and systems.
Functions of the management subsystem by removing barriers to innovative development and its relation with the subsystem of management of innovative development can be represented as follows (see Fig. 3).
Describing the management subsystem on removing obstacles to innovative development as a system of specific control types, highlight the following main common features:
Figure 3
Functions of subsystem of management of innovative
development of subjects of national innovation systems
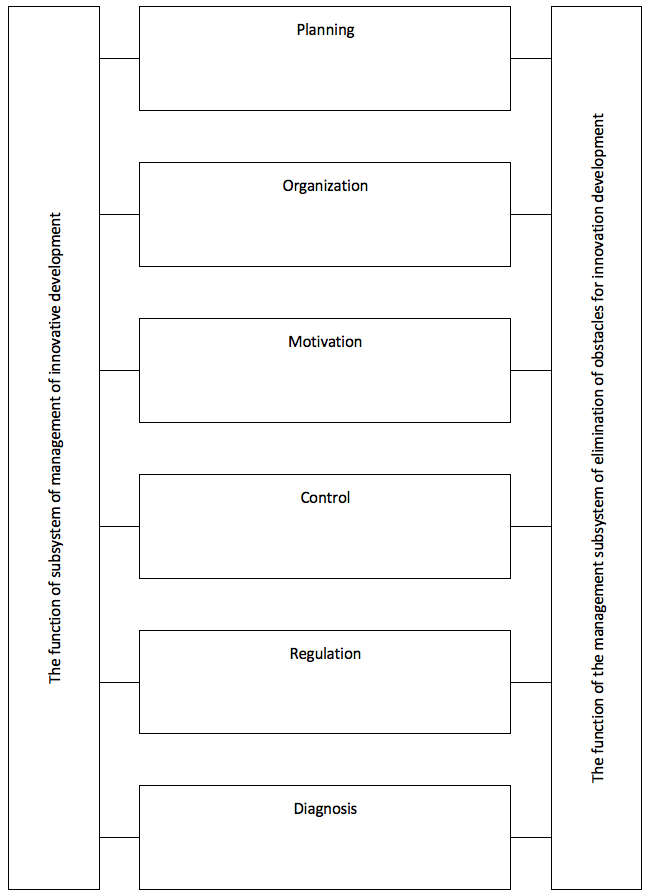
Source: developed by the author.
The essence of management elimination of obstacles for innovation development is reflected in these signs:
To the business entity succeeded in carrying out innovative activities, the Manager should be able to foresee the possibility, the probability of occurrence of various obstacles, prepare for them and to act appropriately to circumstances.
The main task of the subject public administration in a situation of appearance of obstacles for innovation development is to prevent or mitigate the phase of the shock from upcoming obstacles, as well as fast-track adaptation and stabilization of the situation.
According to the proposals set out for the system events management in situations of obstacles to innovative development should contain the following:
Since the emergence of obstacles to the innovative development manifests itself in constant turmoil, periodic changes and phenomena, laws of nature (animate and inanimate). Therefore, the regularities, periodic phenomena and changes there is some benefit, although the obstacles have different sides and quite diverse. This implies that the managers in the management of the removal of obstacles to the innovative development to solve three interrelated problems (Callahan, 2017, p. 43):
Management removing obstacles to innovative development should provide strategic orientation, as the development of the subject of national innovation systems does not have a clearly articulated innovation strategy that is evolutionary in nature, whereas the subject of national innovation systems, which is controllable in accordance with the strategic plan, this development is revolutionary.
Innovative strategy actors in the national innovation systems need to be periodically adjusted, depending on dynamic changes in the environment, functioning and development of subjects of national innovation systems.
Table 1
The process model of innovative development of subjects of national innovation
systems and the sequence of elimination innovative development
The main characteristics of the development |
The main obstacles |
Innovative development based on creativity. This is the stage of the inception of the subject of national innovation systems to its first organizational crisis – the crisis of leadership. |
|
the subject of national innovation systems are conceived and developed thanks to its founders; the focus is on the process of developing product ideas and marketing. |
the organizational structure is not formalized, is based on the intent of the founders; growth of the subject of national innovation systems mostly does not match the level of knowledge and skills possessed by leaders. |
Innovative development based on the principles of competence management |
|
organizational growth after elimination of crisis management; well-planned and regulated the organization of work; involved professional management. |
bureaucratic management structure and a rigid centralization of power limit the creativity of the lower and middle parts; the control system becomes a source of controversy. |
Innovative development based on the principles of delegating managerial powers |
|
the subject of national innovation systems is growing to a size where you to manage them from one Central location is impossible, so there is a delegation of management authority; restructuring of the management system based on decentralization of functions; delegation of authority decision-making; increase of innovative potential of the subject of national innovation systems. |
lack of resource provision of delegated authority. the loss of top management control over the subject of national innovation systems in General. |
Innovative development based on the principles of coordination |
|
change system coordinate the functioning of the units through an automated control system; selection of strategic entities that have a high level of autonomy and empowered to make decisions in the direction of innovation; resource provision decisions taken in respect of innovation. |
contradictions between the functional units and the coordinating centre; increase the length of time the implementation of strategic innovative solutions. |
Innovative development based on the principles of cooperation |
|
increase strategic maneuverability; unification of the team in team; the establishment of common interests and values; the emergence of a new impetus to innovative development. |
the threat of crisis psychological fatigue, when a team can't work as a team; informational uncertainty in the decision-making process and implementation of strategic innovative solutions. |
In other words, in organizations there may be obstacles, namely the crisis – inadequate ways of functioning and development of subjects of national innovation systems and environmental conditions. Hence, it is important for organizations is the statement: inflexible strategic management gives direction to the development of the subject of national innovation systems, but it may occasionally lead to organizational crises.
In a state of organizational crisis innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems mainly arise revolutionary internal changes which in turn lead to raising them to a qualitatively new and higher level of development. Graphic model of the process of innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems, depending on its size through the sequence of removing obstacles to innovative development as follows (see Table 1).
Table 2
Organizational characteristics of the stages of innovative development
Type. Feature |
Innovative development of the entity based on creativity |
Innovative development based on the principles of competence management |
Innovative development based on the principles of delegation, management authority |
Innovative development based on the principles of coordination |
Innovative development based on the principles of cooperation |
Priority management |
Product development, marketing |
Clarity, planning, regulation works |
Increase of innovative potential development |
Strengthen the system of coordination; consolidation |
Strategic agility, problem solving |
The main obstacles to innovation |
The lack of formalization; equivalence scale of the organization and the level of knowledge and skills. |
Bureaucracy, rigid centralization of power; the limitations of creativity; the emergence of contradictions |
The lack of resource provision; control |
Of a disagreement between a Department and a focal point; increase the length of time to implement solutions |
Psychological fatigue; information uncertainty in the adoption of innovative solutions |
The organizational component |
Informal organizational relationships in the middle of a business entity |
Centralized functional elements of organizational structure |
Decentralized organizational relations within the organization |
Group formation, linear scale units |
Teamwork |
Leadership style |
Business |
Authoritarian policy |
Democratic, delegating |
Paternalistic, strict |
Management, based on participation |
Control system |
Market results |
Standards; cost centers |
Reports; profit centres |
Plans; the centers of investment |
Strategic guidelines |
The system of motivation |
Condominium |
Wage growth |
The bonus reward system (individual) |
Profit |
Award for team collaboration |
The last stage describes the logical end of a cycle of innovative development of the subject of national innovation systems. The next step may be restructuring and reorganization, but in the end, the result of the cycle, the direction of the initial stage of development, which is based on creativity.
The General characteristics of each of the stages of innovation development process of a business entity and consistency of the removal of obstacles is given in table. 2.
To successfully overcome the obstacles to innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems need to deeply understand the nature of the specific obstacles, its causes with a view to developing appropriate programmes and activities to overcome them. Quite often it happens that entities ready-to-collision with obstacles and are able to adequately respond to received signals of the occurrence of such situations, phenomena and problems. The system of generation of obstacles in the process of innovation development of an economic entity presented in table 3.
Success in overcoming the phenomena, events and situations that create obstacles to innovative development is possible only with full consideration of the following factors:
Table 3
The system of generation of obstacles for innovation development of economic entities
Option |
Filling |
Surprise. |
The need for innovative development, innovation mainly occurs suddenly. This may occur based on, for example, the emergence of the crisis in the functioning of actors in the national innovation systems, the market introduction of the new product of firm-the competitor, loss of traditional markets its own products, the loss of resources. |
Concern. |
To develop yourself, to enjoy on the side, ready to purchase an innovative project? There are a number of different questions that you need to give a reasoned response, before taking a management decision on the choice of directions of activity of economic entities. |
The lack of information. |
Both the search for answers to pressing questions there are many events, situations which becomes difficult to track information. Information about events and situations that stand in the way of innovative development, creation of innovation is characterized by uncertainty and asymmetry. In the accumulated information, it's hard to distinguish basic, which has the greater impact on innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems. |
The dynamics of events. |
Events arise, change, it is difficult to establish their sequence and relationship. The developments attracted the attention of the external environment (partners, competitors, regulators, the public), appear effects, which were not easy to find adequate answers, and eliminating creativity and disorganized the steps to create and attract innovation. |
The loss of control. |
Low quality of management, which has generally resulted in the emergence of obstacles for innovation development entails a certain loss of control over the situation. Simultaneously, can occur not only uncontrolled events, but the intensive accumulation of information on the progress of the innovation process. |
Strengthening external control. |
Loss of internal control leads to loss of trust and strengthening the external monitoring of resource support for innovative ideas. Is the involvement of external experts, independent auditors, the gain control by the regulatory authorities. |
Lock work. |
The impression is that all are opposed to any innovation works. There is a desire, nobody can say that it was not used against the leadership of the organization. |
Discouragement and panic. |
Appears as depression in the breakthrough innovation of a business entity that gradually develops into a panic of a possible bankruptcy. In this case, it is not easy to convince someone to apply some affirmative action to выведениz subject of national innovation systems from a state of decline. |
Bankruptcy or liquidation of obstacles. |
At this stage there is either the elimination of the subject of national innovation systems, or implementing a program of innovative healing and he has a chance to "survive". |
One of the conditions for effective management of constraints of innovation development is the responsiveness to signals about possible obstacles and threats. Therefore, in our opinion, it is necessary to adhere to these principles control the elimination of obstacles for innovation development:
Therefore, the basis of management constraints to the innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems is the process of continuous tracking of weak signals, interference, which indicate the possibility of emergence and development of negative antiinnovative trends, threats to innovative development.
The analysis gave the opportunity to define what constitutes management of the removal of obstacles to the innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems, identify its purpose and function. Obstacles for the subjects of national innovation systems can take different levels, so this feature highlights the need for various preventive measures for their elimination, which correspond to each stage of the innovation process.
A feature of strategic management subjects of national innovation systems in terms of removing obstacles to innovative development is the need of the formation and implementation of public management different from traditional management in a familiar environment. Management elimination of obstacles should not be limited to classical tasks of public management: changing lines or items, the growth of labour productivity, reduction of search costs of investments and capital markets, restructuring liabilities and assets and so on. Such aspects are subject to the permanent solution and should not depend on the state of activity of the subject of national innovation systems.
Management removing obstacles to innovative development requires that managers conduct unusual and unconventional for a normal state of events, which are associated with certain causes and errors that led to financial and economic difficulties. However, the main difference between effective innovation programs is the increase in risks and related operations, which in usual conditions are unacceptable.
In summary, on the basis of scientific intelligence concerning the examination of obstacles to the innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems that have an impact on competitiveness, we can draw the following conclusions:
1. The analysis of barriers to innovative development of subjects of national innovation systems allowed to reveal that obstacles are a natural phenomenon and should be considered during the management of innovative development and national innovation systems. Based on this classification, phenomena and situations, in order to eliminate obstacles to innovative development and to systematize the causes of these obstacles.
2. The formation of an innovative policy and strategy actors of national innovation systems should be based on identifying obstacles to innovation development. Dedicated controls to eliminate the obstacles to innovative development provide an opportunity to understand the essence of this phenomenon and promote the formation of effective innovation strategies and their subsequent introduction in practice of activity of subjects of national innovation systems.
3. The control subsystem removing obstacles to innovative development should be one of the important places in the practice of actors in the national innovation systems during the justification of actions and measures implementation of management system of subjects of national innovation systems in General. Considered in the study, the objectives, functions, characteristics, subsystem management removing obstacles to innovative development are of practical importance in the solution of problems of formation of organizational and economic instruments the creation of innovative strategy of development of subjects of national innovation systems on the basis of making the best strategic public management decisions.
Under the grant agreement No. 16-27-01001/117-OGON from 12.05.2017 G. international competition RFBR – BRFFR 2017 "the development of the Concept of strategic development of cross-country integration of the national innovation systems of the Union state till 2030".
Abramov, R. A., Sokolov, M. S. (2017) Analysis of the effectiveness of cluster projects of the Union state, Financial law and managemen, 28(1), 18-32.
Bakanova, M., Freinkman, L. (2006). Economic Growth in Belarus (1996–2004): Main Drivers and Risks of the Current Strategy. In L. Vinhas de Souza & O. Havrylyshyn (Eds.), Return to Growth in CIS Countries: Monetary Policy and Macroeconomic Framework. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Bauer, M.W., Knill, C., Eckhard, S. (2017). International Public Administration: A New Type of Bureaucracy? Lessons and Challenges for Public Administration Research. In M. W. Bauer, C. Knill, & S. Eckhard (Eds.), International Bureaucracy: Challenges and Lessons for Public Administration Research. London: Palgrave Macmillan UK.
Butyagin, P.A., Simkin, V.M. (2011). Results from work on the implementation of joint government programs between Belarus and Russia. Fibre Chemistry, 43(4), 267-268. doi:10.1007/s10692-011-9346-8
Callahan, R.F. (2017). Innovation and Tradition in Public Administration Reform. In A. Farazmand (Ed.), Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Chlivickas, E., Melnikas, B. (2016). Training in Public Administration for Globalization and a Knowledge-Based Society with a Humanistic Orientation Human Centered Management in Executive Education. London: Palgrave Macmillan UK.
Czerewacz-Filipowicz, K., Konopelko, A. (2017). The Union State of Russia and Belarus Regional Integration Processes in the Commonwealth of Independent States: Economic and Political Factors. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Kelley, C.S. (2016). Presidential Signing Statements and Public Administration. In A. Farazmand (Ed.), Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Nuti, M. (2007). Belarus: Prototype for Market Socialism? In D. Lane (Ed.), The Transformation of State Socialism: System Change, Capitalism or Something Else? London: Palgrave Macmillan UK.
Pyun, H.-O., Edey Gamassou, C. (2017). Looking for Public Administration Theories? Public Organization Review, 3, 25-29. doi:10.1007/s11115-017-0374-6
Quinot, G. (2016). Private Law and Public Administration. In A. Farazmand (Ed.), Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Rudling, P.A. (2008). Belarus in the Lukashenka Era: National Identity and Relations with Russia. In O. Schmidtke & S. Yekelchyk (Eds.), Europe’s Last Frontier? Belarus, Moldova, and Ukraine between Russia and the European Union. New York: Palgrave Macmillan US.
Savchishina, K.E. (2014). Cenarios of economic development in Belarus in the medium term taking into account the influence of external factors: Model tools and predicted results. Studies on Russian Economic Development, 25(4), 409-422. doi:10.1134/s107570071404011x
Smorgunov, L. (2016). From Public Administration Reform to E-Government: Russian Path to Digital Public Services. In A. V. Chugunov, R. Bolgov, Y. Kabanov, G. Kampis, & M. Wimmer (Eds.), Digital Transformation and Global Society: First International Conference, DTGS 2016, St. Petersburg, Russia, June 22-24, 2016, Revised Selected Papers. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Sokolov M.S. (2017). Strategic management of the integration of the national innovation systems of the Union State: problems and prospects, The proceedings of the annual forum of young strategists, 1(1), 11-16.
Stroev, E.S., Bliakhman, L.S., Krotov, M.I. (1999). CIS Countries on the way to Regional Economic Integration Russia and Eurasia at the Crossroads: Experience and Problems of Economic Reforms in the Commonwealth of Independent States. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Titu, M. A., Bucur, A. (2016). Models for quality analysis of services in the local public administration. Quality & Quantity, 50(2), 921-936. doi:10.1007/s11135-015-0183-3
Ugyel, L. (2016). Paradigms of Public Administration Paradigms and Public Sector Reform: Public Administration of Bhutan. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Vymyatnina, Y., Antonova, D. (2014). Business Cycles Synchronization of Russia, Belarus, and Kazakhstan Creating a Eurasian Union: Economic Integration of the Former Soviet Republics. New York: Palgrave Macmillan US.
White, S., Feklyunina, V. (2014). Belarus and ‘Europe’: Elite Discourses Identities and Foreign Policies in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus: The Other Europes. London: Palgrave Macmillan UK.
Yekelchyk, S. (2008). Out of Russia’s Long Shadow: The Making of Modern Ukraine, Belarus, and Moldova. In O. Schmidtke & S. Yekelchyk (Eds.), Europe’s Last Frontier? Belarus, Moldova, and Ukraine between Russia and the European Union. New York: Palgrave Macmillan US.
1. Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, Department of State and Municipal Management, Russian Economic University named after G.V. Plekhanov; Russian Federation, E-mail: abramovra@rea.ru
2. Doctor of Political Sciences, Professor, Department of Political and Social Science, Russian University of Economics named after G.V. Plekhanov; Russian Federation, E-mail: 160957@mail.ru
3. Candidate of Economic Sciences, Associate Professor, Department of State and Municipal Management, Russian University of Economics named after G.V. Plekhanov; Russian Federation, E-mail: maxim-sokolof@mail.ru
4. Assistant, Department of State and Municipal Management, Russian Economic University named after G.V. Plekhanov; Russian Federation, E-mail: lerapir@yandex.ru