

Vol. 38 (Nº 41) Año 2017. Pág. 2
Nubia Isabel DIAZ Ortega 1; Juan Manuel VILLAMIZAR Ramírez 2
Recibido: 31/03/2017 • Aprobado: 15/04/2017
4. Analysis and discussion of results
ABSTRACT: The accounting information system is considered today as a factor that offers competitiveness to organizations, the present investigation had as purpose to analyze the degree of influence of the use of the accounting information system in the decision-making of Cúcuta SME´s. The empirical study was carried out in the SMEs of the city of Cúcuta in the supermarket sector. By means of the regression analysis in the SSPS software. The results show the high influence of the use of the information of the accounting information system in the decision-making in these companies |
RESUMEN: El sistema de información contable es considerado hoy en día como un factor que ofrece competitividad a las organizaciones, la presente investigación tuvo como propósito analizar el grado de influencia del uso del sistema de información contable en la toma de decisiones de Pymes de Cúcuta. El estudio empírico se realizó en las PYMES de la ciudad de Cúcuta en el sector de supermercados. Por medio del análisis de regresión en el software SSPS. Los resultados muestran la alta influencia que tiene el uso de la información del sistema de información contable en la toma de decisiones en estas empresas. |
In a world with accelerated technological innovation, with easy access to information and communication technologies, business information systems are relevant. The accounting information system within an organization plays an important role as an instrument of continuous improvement, widely used as an element that gives a competitive advantage necessary to face an increasingly aggressive competition.
At the same time, accounting is a valuable tool for evaluating the efficiency of management in collecting the economic facts produced by the organization, it´s data are used permanently in business decision-making. In this context, the systematized accounting information system offers immediate results with a greater capacity and speed of response, improving the effectiveness of management. In addition, from the point of view that decision-making is a process in which the manager must decide for the best choice, the information of immediate access is essential since facilitating the results improves the results.
Therefore, it is pertinent to carry out studies focused on providing information on the variables related to the use of the accounting information system, as well as aspects related to decision-making in the different organizations. Thus, the general objective of the study was to analyze the degree of influence of the use of the accounting information system in the decision-making of SME´s in Cúcuta, in the supermarket sector. Accounting as a key element for organizations to improve their competitiveness, makes it essential to carry out studies on the effect that has in its context.
In the late 1970’s and early 1980´s a proliferating number of thinkers such as John Naisbitt 1982 with Megatrends, Alvin Tofler 1979 with The Third Wave, Fritz Machlup in 1962 with Knowledge is creation, distribution and economically significant; Augmented an era of industrialization based on a highly technological civilization, a new era known as information society or knowledge society Drucker, (2004), Unesco, (2005), Quiroz, (2012). Consequently, modern life has been transformed during the last decades because of the easy access to information, the use of communication technologies, the overcrowding of the internet, phenomena that have change the way of the work, education, culture, production systems, among others. Similarly, the impact on business life is evident, turning it into a systematized management of human resources, technological resources and institutional policies (Garmendia, 2003). Information systems are one of the most relevant elements in the current business environment (Almazan, Medina & Sánchez, 2015). Per this, it can be inferred that one of its advantages is the ease with which information can travel rapidly over gigantic distances (Mueller, Gernon & Meek, 1999), that is, immediate access to information is incorporated.
The information systems allow to streamline and optimize all the processes of the companies, within them to unleash the financial and accounting function impacted by events such as "globalization of the economy, the development of telecommunications and computer technology, new forms of Organization of companies. "Cardona & Zapata (2004) arises a new accounting structure. As an integrator of the information system of the companies, the accounting information system has evolved with ICT in the technical aspect, structure and development. (Méndez, 2008) Therefore, with the passage of time accounting has migrated from a manual accounting to be systematized in many cases. From this it follows that the systematized accounting information system has gained a relevant role as it is the basic tool of managerial work and the gathering of the economic facts of the organization with a faster and updated register. (Diez, 2008). Consequently, other authors define the accounting information system as a collection of data and accounting processing procedures that generate the necessary information to users Medina & Aguilar (2013) to give orientation to activities and improve efficiency organization.
Similarly, the change also reached small and medium enterprises, in recent decades the evidence shows the use of computer accounting systems (Medina & Aguilar, 2013). Likewise, the advances that have been observed in the technologies of the computer systems and of the communication systems have their own impact (Romero, 2013) in the companies to the point that they become indispensable for an efficient administration of the information. The companies have as fundamental consideration the use of technological tools that support the operational and strategic activities of the business. (Guerrero, 2015). Similarly, companies must rely on a robust database, information technology systems can produce financial statements doubly maintaining security and reliability. (Rodríguez, 2015).
SME´s use an accounting information system with the objective of generating the necessary information for the different users and giving a benefit to the organization. The use variable refers to the inclusion of the information generated by the system in the company's decision-making processes, that is, it is not only a question of having the systematized accounting system but also of using it to support managerial decisions, the strategic management of top management to achieve business success. (Astudillo, 2008).
In this order of ideas, the use of accounting information through technology has been shown to have positive effects on the performance of the organization. In other words, the analysis of accounting information should allow the evaluation of the degree to which a company's financial information system captures it´s reality and enables it to assess the quality of its information, risk and growth. (Palepu, Healy & Bernard, 2002). The accounting information and the information system that produces it contribute to the competitiveness of the organization, require a synergy to ensure relevance, timeliness and quality of information (Rueda & Bello, 2009). Other researchers diagnose use through specific characteristics, Auner & Rouhonen (1997) analyze the use of the information system by checking its frequency and type, Markus and Keil (1994) whether it is friendly to the user and to their satisfaction.
One of the important administrative functions is decision-making, therefore, is a very frequent issue in administration, is a main focus of business actions aimed at its study and application. Appreciated under the approach of Drucker (2006), decision-making is the first administrative skill, most of the success of the management of the managers stems from a correct decision-making. A good or bad decision will negatively or positively affect the organization, as well as, it will also have consequences on the achievement of organizational goals, objectives and policies. The manager is dedicated to making real-time decisions on innumerable issues, such as planning, execution, control and evaluation of results, aspects of which are usually measured. In this framework Kinicki and Kreitner (2005) define decision making to an end, which consists in identifying and choosing between alternative solutions that lead to a desired state of affairs. It is one of the main responsibilities of the managers and the quality of the same is very important to achieve a good positioning of the organization.
Decision-making, per Franklin and Krieger (2011), is an important component in the management of organizations, the development of decision-making is conceived as the brain and nerve center of the organization. It defines decision-making as a process by which it is sought to define the nature of a need, a problem or an opportunity, to generate alternative solutions, to evaluate them and finally to select among the available alternatives.
Similarly for Herrera (2008), decision-making can be defined in three ways; First, as the choice of only one alternative of a set of decision options, according to the rational optics of a decision maker, second is a process of elimination of alternatives with the exception of that considered to better meet the objectives and third is the processing of data and information for the purpose of defining with which or which instructions a system eliminates deviations in its operation or can improve it.
Per Kinicki and Kreitner (2005), Robbins (2009), Herrera (2008) and Franklin and Krieger (2011), the decision-making concept is associated with the choice of an alternative. Decision-making is a reality every day, in many ways influenced by the multiple alternatives to choose for the same situation against which the criteria to substantiate them should be analyzed. For entrepreneurs, it is essential to incorporate the information of immediate access, having the immediate results will improve the decisions. People who must make decisions are lacking information online, advance blindly (Quirós, 2012).
Within the information systems that support the decision-making process the classification made by O'Brien & Marakas 2006, considers accounting a managerial administrative support subsystem used for management decision-making. Because it is demonstrated that accounting is an information system whose purpose is to provide financial information to management, third parties and external and internal users of the financial statements per their information needs, therefore, allows them to make judgments and take Decisions.
Accounting has been constituted as a basic source of information for the decision-making process in companies (Sinisterra, Polanco & Henao, 2011). In the same way, accounting is a control tool, it serves to issue financial statements for decision-making purposes and determine the utility that would help a company in each period. (Polo, 2013). Also, it aims to produce reports, which analyzed and interpreted, allow to plan, control and make decisions about the activity of the company. (Coral & Gudiño, 2014). In addition, accounting and financial information constitute the universal language of business and offer the user various tools to make the most essential decisions, (Cuellar, Vargas & Castro, 2016). It also helps decision-making by showing where and how the money has been spent or commitments have been made. (Zapata, 2011).
Attending to the revised literature, it is concluded in a scenario where the predominant tendency is the globalization of accounting, the accounting information system plays an important role in guiding the future course of business, becoming the permanent support of the decision-making. Therefore, the hypothesis raised by this research is how the use of information from the accounting information system contributes positively to better decision-making.
In these times of so much technology, the accounting information system is not far behind, since the information generated by them is used to improve the results of organizations. The objective of this research is to determine the influence that the use of the information has on the decision-making of the users of the company. Initially, a review of the theoretical framework on the variables under study, independent variables, use of information and dependent variable: decision making was performed.
Then, a questionnaire was used to collect the data, which was submitted to expert judgment. The questionnaire included aspects about the use of accounting information and decision-making, the total of items was 31 which included 8 selection questions Multiple and 23 questions assessed on the Lickert scale. (Always, almost always, sometimes, almost never and never). The validated questionnaire was then applied to the users of the accounting information system. For the determination of the sample was taken as a population to the existing supermarkets in the city of Cúcuta, data provided by the Chamber of Commerce of Cúcuta obtaining a total population of 118 supermarkets. The construction of the sample was based on the level of satisfaction of the accounting software in the research entities, a 95% confidence level was sought with a significance level of 5% and a margin of error of 5% for the sample Consolidated was 30 supermarkets.
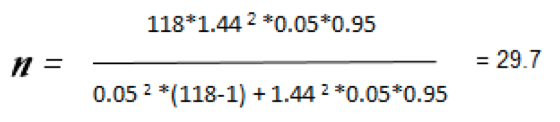
Later, based on the results obtained, the general description and inferential analytical is derived by means of the regression analysis with the SSPS version 21, in order to verify the hypothesis designed. Finally, the development of the conclusions was derived based on the analysis of the results obtained. Likewise, the minimum values accepted for the reliability of the items will be the Combrach Alpha of 0.80 or higher, following the criteria of George and Mallery (2003).
First, the descriptive analysis was performed. This stage of the research is directed to study the statistical data considering the measure of central tendency the arithmetic mean in each of the research questions, obtaining a result of 4.28 in the total of the items by which it is inferred a high utilization of the Accounting information system as a tool for decision-making. All the companies studied have a system of accounting information systematized, the results indicate that 47% acquired it between 1 to 5 years, 40% for more than 5 years and 13% more recently between 1 and 6 months, in all the cases are a standardized commercial package, not made per the special information needs of each company. The expenses incurred in the maintenance, updating and training carried out by the companies in the accounting information system showed that 27% of the supermarkets spend between 2,000,000 and 2,500,000, 23% between 3,000,000 and 4,000,000, 17% less than 2,000,000 and 13% between 4,000,000 and 5,000. Accounting software is fed by 80% of the female sex and 20% of the male sex.
It should be noted that supermarkets in Cúcuta have an accounting information system with integrated software that make high use, however, in issues such as the accompaniment that accounting information requires to improve the results of the organization, yielded a moderate average with a score of 3.83. Also to the question about the weaknesses of the information system, stands out with 34% of respondents stated that more managerial reports are missing. The previous review warns that supermarkets use the accounting information system, however, there are aspects to improve such as monitoring business results and developing more managerial reports.
Second, inferential analysis was developed. In this phase of the research the results of reliability are presented with a result of the Combrach Alpha index of 0.882 for the variable use of the accounting information system and of 0.861 for the variable decision-making. It can be noted that the variables are in the accepted ranges and the questionnaire in general reaches 0.903.
As for the relation obtained in the hypothesis under study, the explanatory variance and the level of significance are taken using the Student test. Hypothesis H1, use of information and decision making an R of 0.629, an R2 of 0.395 and a significance of 0.029. As the hypothesis is observed, it accepts the three criteria, so it is stated that the use of the accounting information system helps to make better decisions.
The objective of the present investigation was to determine the degree of influence of the use of the accounting information systems of the small and medium companies of the sector of supermarkets of Cúcuta that supports them in the decision-making.
From the results obtained it was possible to conclude that having a good accounting information system is important in SMEs, so they have systematized systems used to generate accounting and financial reports. The use of these systems has allowed to accompany the decision-making process, the information is used to evaluate alternatives and make decisions in a faster and more effective way. Finally, it is observed that accounting information must be aligned with the objectives established by the administration to take advantage of it in a deeper way per the needs of the management. In fact, it is possible to recommend the use of software to the measure of each company elaborated per the specifications of the same ones.
Almazan, D, Medina, J. & Sánchez, M. (2015). Los sistemas de información en el desempeño organizacional: Un marco de factores relevantes. Revista investigación Administrativa. Vol. 115. Recovered in: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Monica_Sanchez_Limon/publication/297038361_Los_sistemas_de_informacion_en_el_desempeno_organizacional_Un_marco_de_factores_relevante/links/56dcbe5008aebabdb41428e9.pdf
Astudillo, M. (2008). Consideraciones para la selección de sistemas de información contables y administrativos. Revista Entramado. Universidad Libre. Vol. 4. Cali.
Auer, T & Rouhonen, M. (1997). Analysing the quality of USE an management in the organizational context. Experiencies from two cases. Information Resources Management Journal, Vol. 10.
Cardona, J. y Zapata, M. (2004). Estandartes internacionales para la formación del contador público. Journal Contaduría University of Antioquia. Vol. 44 (Jan-Jun.) pág. 151-175.
Coral, L. & Gudiño, E. (2014). Contabilidad Universitaria. Editorial Mc Graw Hill. Bogotá.
Drucker, P (2004). La sociedad post-capitalista. Editorial group Norma. Bogotá.
Drucker, P (2006). Harvard Business Review. La Toma de Decisiones. Editions Deusto. Editorial Planeta Colombia S.A. Bogotá.
Estupiñan, R. (2013) NIC/NIIF. Transición y adopción en la empresa. Implementación por primera vez de las NIIF Plenas y de la NIIF para las PYMES. Editions of the U. Bogotá.
Franklin, E. y Krieger, M. (2011). Comportamiento Organizacional. Enfoque para América Latina. Editorial Pearson. Prentice Hall. México.
George, D. y Mallery, P. (2003). SPSS for Windows step by step: A Simple Guide and Reference. 11.0 Update. Boston: Allen y Bacon.
Garmendia, L. (2003). Sociedad de la información y gestores de información. Journal Biblios. Vol. 16.
Guerrero, J. (2015). Normas Internacionales de Información Financiera-NIIF: responsabilidad de la alta gerencia: consideraciones básicas y experiencias en la adopción. University Externado Of Colombia.
Herrera, M. (2008). Toma de decisiones en ambientes turbulentos. Modelos y herramientas para las ciencias de la complejidad. University Autónoma Of Baja California. México.
Kinicki, A y Kreitner R, (2005) Comportamiento Organizacional, conceptos, problemas y prácticas. Editorial Mc Graw Hill, México D.C.
Medina J. & Aguilar, P. (2013) Administración y calidad de la información de los sistemas de información contable de las PYMES. Journal Cuadernos de Administración. University From Valle. Vol. 29 No 49. Ene-Jun., 2013.
Markus, M & Keil, M. (1994). If we build it, they will come: designing information systems that people want to use. Sloan Management Review, Vol. 35.
Méndez, M (2008). El impacto de las TIC en la información contable empresarial. Revista Revista Economía Industrial. Universidad Complutense de Madrid. Recovered in: http://eco.mdp.edu.ar/cendocu/repositorio/00902.pdf
Mueller, G., Gernon, H & Meek, Gary (1999). Contabilidad una perspectiva internacional. Editorial Mc Graw Hill. México.
O´Brien, J. & Marakas, G. (2006). Sistemas de información gerencial. Editorial Mc Graw Hill. México.
Polo, B. (2013). Contabilidad de Costos en la Alta Gerencia. Group Editorial Nueva Legislación. Bogotá.
Rincón, C. (2015). Guía para elaborar plan de cuentas con NIIF. Taxonomía contable vs. Tesauro contable. Editions of the U. Bogotá.
Rodríguez, C. (2015) Estado de Situación Financiera de Apertura para NIIF PYMES. ¿Que hacer y como hacerlo? Institute Colombian of Tax Studies. Medellín.
Romero, a. (2013). Contabilidad práctica para no contadores. Editorial Mc Graw Hill. México.
Rueda, G & Bello, M. (2009). Los sistemas de información contable en la administración estratégica organizacional. Cuadernos de Contabilidad. Pontificia University Javeriana. Vol. 27.
Shing, N. (2001). The Impact of Information Technology and Financial Performance: The Importance of Strategic Choice. Europ. The Journal OF Information System. Vol. 10 (4) pág. 227-236.
Sinisterra, G., Polanco, L, & Henao, H. (2011). Contabilidad Sistema de información para las organizaciones. Editorial Mc Graw Hill. Bogotá.
UNESCO, (2005). Hacia las sociedades el conocimiento. Informe mundial. Recovered from: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001419/141908s.pdf
Quirós, J. (2012). Etapas de la Pyme. Transforme su esfuerzo en inteligencia directiva. Editions Díaz de Santos. Madrid.
Quiroz, F. (2012). Sociedad de la información y del conocimiento. Boletín de los sistemas Estadísticos y de Información Geográfica. Recovered from: http://seieg.iplaneg.net/seieg/doc/sociedad_1396044378.pdf
Zapata, P. (2011). Contabilidad general. Con Base en la NIIF. Editorial Mc Graw Hill. México.
1. Teacher University of Pamplona Faculty of Economics. Member of the CEYCON research group. Email: ndiaz712@hotmail.com
2. Teacher University of Pamplona Faculty of Economics. Member of the GRAMMY research group. Email: juan.villamizar@unipamplona.edu.co