

 Vol. 39 (Number 12) Year 2018. Páge 15
Vol. 39 (Number 12) Year 2018. Páge 15
Sofia L. LEBEDEVA 1; Olga S. SEMKINAS 2
Received: 01/11/2017 • Approved: 30/11/2017
ABSTRACT: The purpose of the article is to develop the strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy. Volgograd Oblast has been selected as the objects of the research. For assessing the influence of risk component on the process of formation of innovations-oriented economy in Volgograd Oblast, the authors study intermediary results of implementation of the Strategy of socio-economic development of Volgograd Oblast until 2025. They are studied with the help of the methodology of time series analysis. The main conclusion of the research is that in addition to high risk level, which accompanies innovational activity, additional risks emerge in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy. This leads to high risk component, which is a serious obstacle in this process. The authors perform assessment of the risk component on the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy by the example of Volgograd Oblast, determine the key risks that emerge in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy, and develop the strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy. |
RESUMEN: El objetivo del artículo es desarrollar la estrategia de gestión de riesgos en el proceso de formación de una economía regional orientada a la innovación. Volgograd Oblast ha sido seleccionado como el objeto de la investigación. Para evaluar la influencia del componente de riesgo en el proceso de formación de la economía orientada a las innovaciones en el Óblast de Volgogrado, los autores estudian los resultados intermedios de la implementación de la Estrategia de desarrollo socioeconómico del oblast de Volgogrado hasta 2025. Se estudian con la ayuda del metodología de análisis de series de tiempo. La principal conclusión de la investigación es que, además del alto nivel de riesgo, que acompaña a la actividad innovadora, surgen riesgos adicionales en el proceso de formación de una economía regional orientada a la innovación. Esto conduce a un componente de alto riesgo, que es un obstáculo serio en este proceso. Los autores realizan una evaluación del componente de riesgo sobre el proceso de formación de una economía regional orientada a la innovación mediante el ejemplo de Volgograd Oblast, determinan los riesgos clave que surgen en el proceso de formación de una economía regional orientada a las innovaciones y desarrollan la estrategia de riesgo gestión en el proceso de formación de una economía regional orientada a la innovación. |
Under the pressure of global competition, the tendency for formation of innovations-oriented economy was distributed to the regional level of economic systems. Russia’s regions adopted the strategy of innovational socio-economic development, but the first results were not satisfactory. Instead of quick growth and innovational development of regional economy, the first half of the time row, given to implementation of these strategies, was marked by ineffective spending of allocated assets of the federal and regional budgets.
In this research, the authors offer the hypothesis that a serious restraining factor on the path of implementation of strategies of modern Russia’s regional economy’s innovational development is high risk component. Our goal in the context of this article consists in development of the strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy.
The object of the research is Volgograd Oblast, as it presents the average statistical Russian region, being neither the donor not the recipient. The set goal should be achieved in the context of successive solution of the following main practical tasks:
For assessment of influence of the risk component on the process of formation of innovations-oriented economy in Volgograd Oblast, the authors study intermediary results of implementation of the Strategy of socio-economic development of Volgograd Oblast until 2025 (Table 1).
Table 1
Dynamics of results of implementation of the Strategy of socio-economic development of Volgograd Oblast until 2025
|
Values of indicators for years, ratio of the current year to 2008, times |
|||||||
|
2010 |
2012 |
2014 |
2016 |
||||
Goal |
Result |
Goal |
Result |
Goal |
Result |
Goal |
Result |
|
Volume of investments into fixed capital in compatible prices |
1.5 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
0.9 |
2.7 |
0.7 |
3.5 |
0.6 |
Volume of expenditures for R&D at the end of the period, as compared to GRP |
1.3 |
1.1 |
1.7 |
1.0 |
2.2 |
0.9 |
3.0 |
0.7 |
Number of innovational companies |
1.6 |
1.1 |
2.1 |
1.5 |
2.8 |
1.9 |
3.7 |
2.1 |
Share of innovational companies in the total structure of business |
1.2 |
1.1 |
1.4 |
1.2 |
1.9 |
1.4 |
2.3 |
1.9 |
Volume of innovational products |
1.8 |
1.5 |
2.6 |
1.8 |
3.2 |
2.1 |
4.4 |
2.6 |
Share of innovational products in the total structure of production of goods |
1.3 |
1.2 |
1.5 |
1.4 |
1.8 |
1.6 |
2.2 |
2.0 |
Source: compiled by the authors on the basis of: (Volgogradskaya Pravda, 2008),
(Federal State Statistics Service, 2016).
They are studied with the help of the methodology of time series analysis. Table 1 contains the results of trend analysis of dynamics of these indicators, on the basis of which plan-fact analysis is performed. During the research, the authors use such scientific methods as systemic and logical analysis, synthesis, deduction, induction, and graphic representation of data.
The theory and practice of risk management of regional economy development are discussed in the works (Popkova, 2013), (Belov and Kravets, 2013), (Пржедецкая, 2014), and (Ragulina et al., 2015). Specifics of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy are studied in publication (Pradel-Miquel, 2015), (Wolfe and Gertler, 2016), (Wolfe and Bramwell, 2016), (Harris et al., 2013, (Ibrahim et al., 2014), (Shala et al., 2015), and (Veselovsky et al., 2015).
The performed plan-fact analysis of dynamics of the results of implementation of the Strategy of socio-economic development of Volgograd Oblast until 2025 showed that the achieved results are below the planned results – at that, the difference between the targeted and received results grows with time.
The largest underrun is observed for the volume of investments into fixed capital (83% in 2016, as compared to 33% in 2010) and for the volume of expenditures for R&D as to GRP (77% in 2016, as compared to 16% in 2010). This is explained by increase of deficit of financial resources with companies and regional authorities, which was a reason for reduction of investment activity.
The largest underrun is observed for such indicators as the share of innovational products in the general structure of commodity production (9% in 2016, as compared to 7% in 2010) and the share of innovational companies in the total structure of business (17% in 2016, as compared to 8% in 2010). However, in view of absolute changes of these indicators (without connection to the general structure), the underrun of which constitutes 43% and 41% in 2016, accordingly, this shows reduction of general business activity in the region, not the increase of innovational activity of entrepreneurship.
Thus, inaccessibility of the set targeted values of the indicators of efficiency of the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy in Volgograd Oblast shows the influence of the risk component on this process. Its influence is seen at the corporate (micro) and the regional (meso) levels.
On the one hand, at the corporate level high risk component of innovational activity restrains innovational activity of entrepreneurial structures. It may be characterized in the following way. The state offers stimuli for manifestation of innovational activity (“tax holidays”, subsidies, support for sales of innovational products, etc.).
However, these stimuli cannot be received in practice due to complex procedures of receipt of the announced benefits (large lines, large set of documents, constantly changing requirements, etc.) – institutional risk – or unexpected change of state innovational policy, due to increase of deficit of the regional budget – which leads to cancelling the state measures for stimulation of innovational activity – political risk.
On the other hand, at the regional level the risk component of state innovational policy has not been taken into account at the stage of its development, so there are unexpected risks at the stage of its implementation – which, without proper management, hinder the implementation of this strategy.
Thus, the measures for implementation of the regional innovational policy could be ineffective due to unfair attitude of business to innovative activities, related to copying of existing innovations from rivals or non-implementation of innovations with false accounting on implementation of innovations for receipt of state support – risk of false innovations – and/or due to low innovative activity of business due to lack of possibilities, when state support is not sufficient, and unattractiveness of such support – risk of low demand for stimuli.
It should be noted that this work does not view generally known risks that accompany innovative activity, as our task consists in determination of additional specific risks, peculiar for the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy. In this context, the risks are connected to non-execution of obligations by participants of the relations within the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy (entrepreneurship and state). We offer the following recommendations for management of the determined risks:
According to the above, we developed the following strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy (Fig. 1).
Figure 1
Strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy
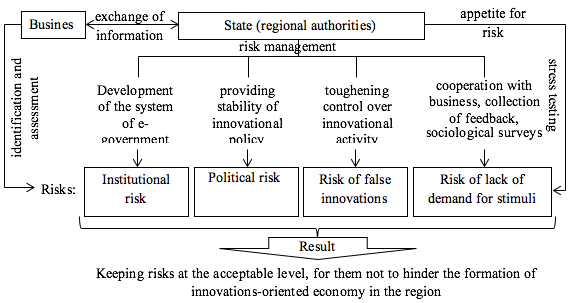
Source: compiled by the authors.
As is seen from Figure 1, business identifies risks, evaluates them, and provides the gathered information to the state (regional authorities). In its turn, it identifies the risks and evaluates their importance through stress testing. If the current level of one, several, or all risks exceeds the set acceptable limits (appetite for risk), which is a function of the state, the corresponding measures in the sphere of managing these risks are implemented. As a result, risks are kept at the acceptable level, for them not to hinder formation of innovations-oriented economy in the region.
Thus, the main conclusion of the research is that in addition to a high level of risks that accompany innovational acitvity, additional risks appear in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy. This leads to a high risk component, which is a serious obstacle in this process. For its normalization, a strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy is offered.
Despite the connection of the performed calculations for verifying the offered hypothesis in the economic practice of Volgograd Oblast, the authors’ conclusions and recommendations are oriented at the Russia’s regional economy on the whole, and the developed strategy of risk management in the process of formation of innovations-oriented regional economy is accessible for implementation in any region of modern Russia.
Belov, A.G., Kravets, A.G. (2013). Business performance management in small and medium businesses and functional automation. World Applied Sciences Journal, 24 (24), pp. 7-11.
Harris, R., McAdam, R., McCausl, I., Reid, R. (2013). Knowledge management as a source of innovation and competitive advantage for SMEs in peripheral regions. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, 14(1), с. 49-61.
Ibrahim, S., Sukeri, S.N., abd. Rashid, I.M. (2014). Factors influencing the diffusion & implementation of management accounting innovations (MAIS), Malaysian manufacturing industries in Northern Region. Advances in Environmental Biology, 8(9 SPEC. ISSUE 4), с. 504-512.
Popkova, E.G. (2013). Marketing strategy то overcome the "underdevelopment whirlpool" of the Volgograd region. Conference of the Eurasia-Business- and-Economics-Society (EBES). Russian Acad Sci, Inst Econ, Ural Branch, Ekaterinburg, RUSSIA publ.: SEP 12-14, 2013, pp. 52-61.
Pradel-Miquel, M. (2015). Making polycentrism: Governance innovation in small and medium-sized cities in the West Midlands and Barcelona metropolitan regions. Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy, 33(6), с. 1753-1768.
Ragulina, Y.V., Stroiteleva, E.V., Miller, A.I. (2015).
Modeling of integration processes in the business structures
Modern Applied Science, 9 (3), pp. 145-158.
Shala, M., Hajrizi, E., Hoxha, V., Stapleton, L. (2015). Cost-Oriented Agile Innovation for Mechatronics Management in Less Developed Regions. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48(24), с. 150-152.
Veselovsky, M.Y., Pogodina, T.V., Idilov, I.I., Askhabov, R.Y., Abdulkadyrova, M.A. (2015). Development of financial and economic instruments for the formation and management of innovation clusters in the region.Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(3), с. 116-123.
Wolfe, D., Bramwell, A. (2016). Innovation, creativity and governance: Social dynamics of economic performance in city-regions. Innovation: Management, Policy and Practice, 18(4), с. 449-461.
Wolfe, D.A., Gertler, M.S. (2016). Growing urban economies: Innovation, creativity, and governance in Сanadian city-regions. Growing Urban Economies: Innovation, Creativity, and Governance in Canadian City-Regions, с. 1-420.
Volgogradskaya Pravda (2008). The Law of Volgograd Oblast dated November 21, 2008 No. 1778-od “Regarding the strategy of socio-economic development of Volgograd Oblast until 2025”. URL: http://docs.cntd.ru/document/819076044 (data accessed: 23.06.2017).
Przhedetskaya N.V. (2014). Designing marketing management of the innovational model of education in the conditions of development economy. Bulletin of Tula State University, 4 (1).
Federal State Statistics Service; (2016). Regions of Russia. Socio-economic indicators. 2016: statistical bulletin. Moscow: Federal State Statistics Service.
1. Institute of Economics and Finance, Moscow State University of Railways Engineering. Moscow, Russia
2. Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia